Contents
- 1. 파이썬 두 리스트 비교하기
- 2. 파이썬으로 html 파일 만들기
- 3. 파이썬 리스트 순서 뒤집기
- 4. 파이썬 리스트 요소 삭제하기
- 5. 파이썬 두 문자열 비교하기 (difflib)
- 6. 파이썬 문자열 앞을 0으로 채우기
- 7. 파이썬 문자열 찾기
- 8. 파이썬 모든 문자열 찾아서 바꾸기
- 9. 파이썬 문자열 결합, 분리하기
- 10. 파이썬 문자열 포맷팅하기
- 11. 파이썬 리스트 슬라이싱 활용하기
- 12. 파이썬 리스트 길이 제한하기
- 13. 파이썬 조건문 간단하게 표현하기
- 14. 파이썬 with 문으로 파일 열고 닫기
- 15. 파이썬 enumerate() 사용하기
- 16. 파이썬 zip() 사용하기
- 17. 파이썬 튜플 언패킹하기
- 18. 파이썬 변수 바꾸기 (swap)
- 19. 파이썬 딕셔너리에서 값 얻기
- 20. 파이썬 출력 결과 저장하기
- 21. 파이썬 폴더 생성하기
- 22. 파이썬 시간 측정하기
- 23. 파이썬 int() 함수 사용하기
- 24. 파이썬 float() 함수 사용하기
- 25. 파이썬 리스트 만들기
- 26. NumPy 어레이 슬라이싱 활용하기
- 27. NumPy 어레이 한 줄에 출력하기
- 28. NumPy 어레이 요소 바꾸기
- 29. NumPy 어레이 정렬 (np.argsort)
- 30. NumPy 어레이 연결, 분리하기
Tutorials
- Python Tutorial
- NumPy Tutorial
- Matplotlib Tutorial
- PyQt5 Tutorial
- BeautifulSoup Tutorial
- xlrd/xlwt Tutorial
- Pillow Tutorial
- Googletrans Tutorial
- PyWin32 Tutorial
- PyAutoGUI Tutorial
- Pyperclip Tutorial
- TensorFlow Tutorial
- Tips and Examples
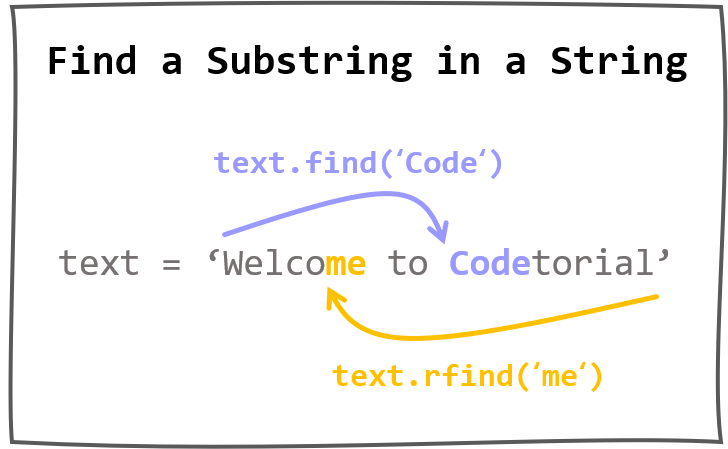
7. 파이썬 문자열 찾기¶
파이썬은 문자열 안에서 문자열의 위치를 찾기 위한 다양한 방법을 제공합니다.
이 페이지에서는 예제와 함께 find(), index(), rfind(), rindex() 메서드를 소개합니다.
find()¶
예제¶
text = 'Welcome to Codetorial'
pos_e = text.find('e')
print(pos_e)
pos_Code = text.find('Code')
print(pos_Code)
pos_code = text.find('code')
print(pos_code)
1
11
-1
find(‘e’)는 처음으로 발견되는 문자 ‘e’의 위치를 찾아서 1을 반환합니다.
마찬가지로 find(‘Code’)는 처음으로 발견되는 문자열 ‘Code’의 위치인 11를 반환합니다.
find(‘code’)는 문자열 ‘code’의 위치를 찾습니다. 대소문자를 구분하기 때문에 ‘code’를 찾지 못해서 -1를 반환합니다.
index()¶
예제¶
text = 'Welcome to Codetorial'
pos_e = text.index('e')
print(pos_e)
pos_Code = text.index('Code')
print(pos_Code)
pos_code = text.index('code')
print(pos_code)
1
11
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/Users/python/tips_and_examples/test.py", line 9, in <module>
pos_code = text.index('code')
ValueError: substring not found
index()는 문자열 안에서 문자 또는 문자열을 찾는 면에서 find()와 거의 비슷합니다.
하지만 find()와 달리, index()는 문자 또는 문자열을 찾지 못할 경우 예외를 발생합니다.
rfind()¶
예제¶
text = 'Welcome to Codetorial'
pos_e_last = text.rfind('e')
print(pos_e_last)
pos_e_first = text.find('e')
print(pos_e_first)
pos_to_last = text.rfind('to')
print(pos_to_last)
pos_to_first = text.find('to')
print(pos_to_first)
14
1
15
8
rfind()는 find()와 다르게 문자열의 끝에서부터 처음으로 발견되는 문자 또는 문자열의 위치를 반환합니다.
문자열을 찾지 못할 경우 -1을 반환합니다.
rindex()¶
예제¶
text = 'Welcome to Codetorial'
pos_Code_last = text.rindex('Code')
print(pos_Code_last)
pos_code_last = text.rindex('code')
print(pos_code_last)
11
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/Users/python/tips_and_examples/test2.py", line 6, in <module>
pos_code_last = text.rindex('code')
ValueError: substring not found
rindex()는 rfind()와 마찬가지로 문자열의 끝에서부터 처음으로 발견되는 문자 또는 문자열의 위치를 반환합니다.
하지만 index()와 같이 rindex()는 문자열을 찾지 못할 경우 예외를 발생합니다.
파이썬 문자열 기초와 다양한 메서드는 Python 문자열 (Strings) 페이지를 참고하세요.
이전글/다음글
이전글 : 6. 파이썬 문자열 앞을 0으로 채우기
다음글 : 8. 파이썬 모든 문자열 찾아서 바꾸기