Contents
- 강화학습 시작하기 (CartPole 게임)
- 환경 (Environments)
- 관찰 (Observations)
- 공간 (Spaces)
- 첫번째 알고리즘
- 첫번째 뉴럴 네트워크
- 강화학습 (Reinforcement Learning)
- Q-learning
- Deep Q-learning
- Epsilon-greedy 정책
- 첫번째 훈련
- Epsilon의 영향
Tutorials
- Python Tutorial
- NumPy Tutorial
- Matplotlib Tutorial
- PyQt5 Tutorial
- BeautifulSoup Tutorial
- xlrd/xlwt Tutorial
- Pillow Tutorial
- Googletrans Tutorial
- PyWin32 Tutorial
- PyAutoGUI Tutorial
- Pyperclip Tutorial
- TensorFlow Tutorial
- Tips and Examples
Epsilon의 영향¶
앞의 예제에서 뉴럴 네트워크를 훈련하는데 \(\epsilon\)-greedy 정책을 사용했습니다.
이 페이지에서는 훈련 과정에서 탐색 (exploration)과 활용 (exploitation)의 조절이 학습 결과에 어떤 영향을 미치는지 비교해봅니다.
import gym
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import random
from collections import deque
# 뉴럴 네트워크 모델 만들기
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Dense(24, input_dim=4, activation=tf.nn.relu),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(24, activation=tf.nn.relu),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(2, activation='linear')
])
# 모델 컴파일
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='mean_squared_error',
learning_rate=0.001)
score = []
memory = deque(maxlen=2000)
# CartPole 환경 구성
env = gym.make('CartPole-v0')
# 1000회의 에피소드 시작
for i in range(1000):
state = env.reset()
state = np.reshape(state, [1, 4])
eps = 1 / (i / 50 + 10)
# 200 timesteps
for t in range(200):
# Inference: no e-greedy
predict = model.predict(state)
action = np.argmax(predict)
# Inference: e-greedy
# if np.random.rand() < eps:
# action = np.random.randint(0, 2)
# else:
# predict = model.predict(state)
# action = np.argmax(predict)
next_state, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
next_state = np.reshape(next_state, [1, 4])
memory.append((state, action, reward, next_state, done))
state = next_state
if done or t == 199:
print('Episode', i, 'Score', t + 1)
score.append(t + 1)
break
# Training
if i > 10:
minibatch = random.sample(memory, 16)
for state, action, reward, next_state, done in minibatch:
target = reward
if not done:
target = reward + 0.9 * np.amax(model.predict(next_state)[0])
target_outputs = model.predict(state)
target_outputs[0][action] = target
model.fit(state, target_outputs, epochs=1, verbose=0)
env.close()
print(score)
\(\epsilon\)-greedy 정책을 사용하지 않고, 뉴럴 네트워크를 훈련하는 코드입니다.
\(\epsilon\)-greedy 정책을 사용했던 앞의 결과와 비교하면 아래와 같습니다.
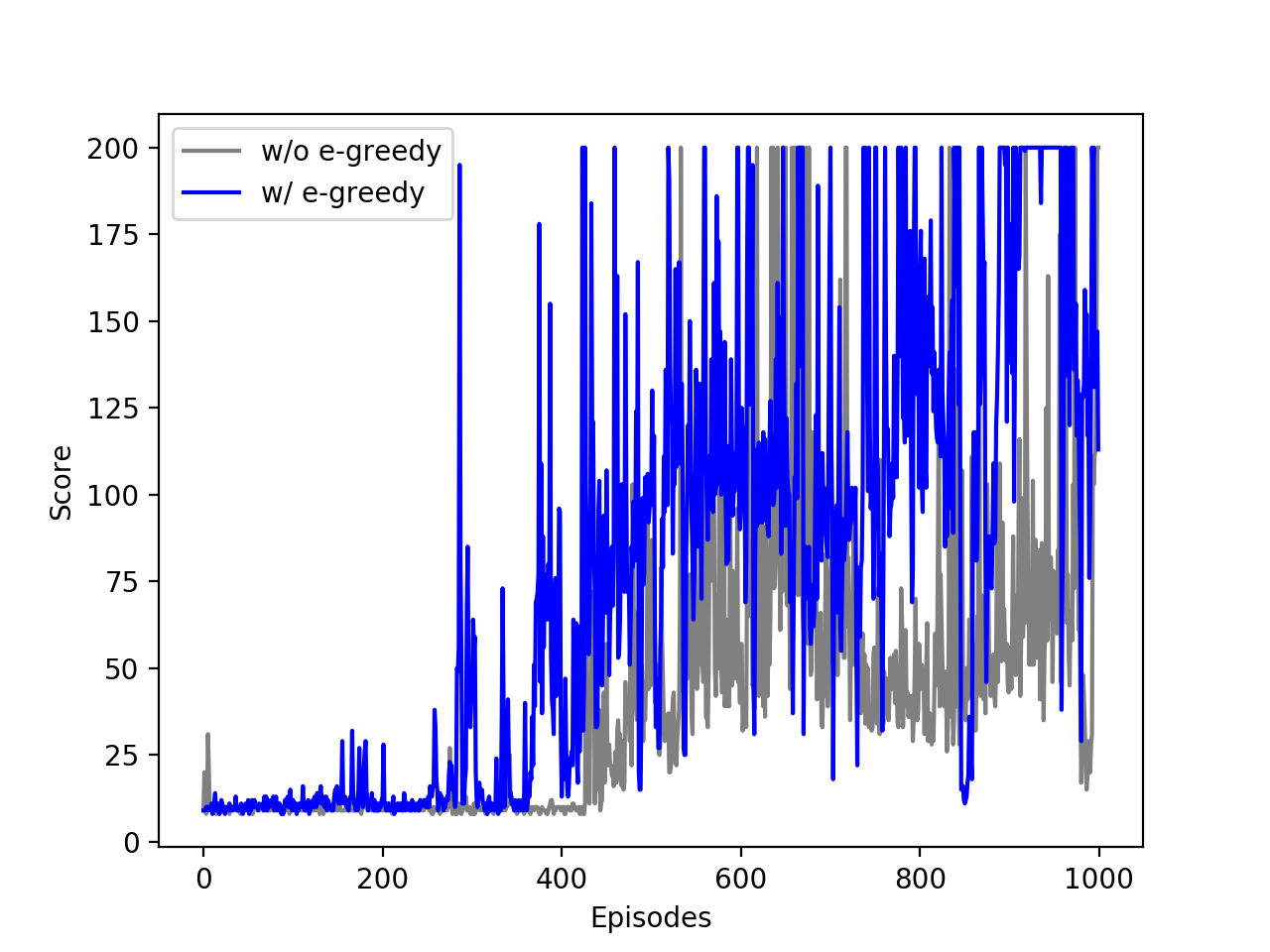
\(\epsilon\)-greedy 정책 유무에 따른 점수 차이.¶
훈련 과정에서 탐색과 활용의 적절한 사용이 결과에 좋은 영향을 미치는 것을 알 수 있습니다.
다시 말해서 훈련 과정에서는 이미 알고 있는 것과 다른, 엉뚱한 선택을 가끔씩 경험해 보는 것이 더 효과적임을 의미합니다.
이전글
이전글 : 첫번째 훈련