Contents
- NumPy - 수학/과학 연산을 위한 파이썬 패키지
- NumPy 기초
- NumPy 어레이 만들기
- NumPy 어레이 출력하기
- NumPy 기본 연산
- NumPy 범용 함수 (ufunc)
- NumPy 인덱싱/슬라이싱/이터레이팅
- NumPy 어레이 형태 다루기
- NumPy 난수 생성 (Random 모듈)
- NumPy 다양한 함수들
- numpy.absolute
- numpy.add
- numpy.allclose
- numpy.amax
- numpy.amin
- numpy.append
- numpy.arange
- numpy.arccos
- numpy.arccosh
- numpy.arcsin
- numpy.arcsinh
- numpy.arctan
- numpy.arctanh
- numpy.argmax
- numpy.argsort
- numpy.around
- numpy.array_equal
- numpy.array_split
- numpy.array
- numpy.cbrt
- numpy.ceil
- numpy.clip
- numpy.concatenate
- numpy.copy
- numpy.cos
- numpy.cosh
- numpy.cumsum
- numpy.deg2rad
- numpy.delete
- numpy.digitize
- numpy.divide
- numpy.dot
- numpy.dsplit
- numpy.empty_like
- numpy.empty
- numpy.equal
- numpy.exp
- numpy.exp2
- numpy.expm1
- numpy.fabs
- numpy.fix
- numpy.floor_divide
- numpy.floor
- numpy.full_like
- numpy.full
- numpy.greater_equal
- numpy.greater
- numpy.hsplit
- numpy.identity
- numpy.insert
- numpy.isclose
- numpy.less_equal
- numpy.less
- numpy.linspace
- numpy.loadtxt
- numpy.log
- numpy.log1p
- numpy.log2
- numpy.log10
- numpy.matmul
- numpy.mean
- numpy.mod
- numpy.multiply
- numpy.ndarray.astype
- numpy.ndarray.flatten
- numpy.ndarray.shape
- numpy.negative
- numpy.nonzero
- numpy.not_equal
- numpy.ones_like
- numpy.ones
- numpy.polyfit
- numpy.positive
- numpy.power
- numpy.prod
- numpy.rad2deg
- numpy.random.rand
- numpy.random.randint
- numpy.random.randn
- numpy.random.seed
- numpy.random.standard_normal
- numpy.reciprocal
- numpy.remainder
- numpy.repeat
- numpy.reshape
- numpy.rint
- numpy.round_
- numpy.savetxt
- numpy.set_printoptions
- numpy.sign
- numpy.sin
- numpy.sinh
- numpy.split
- numpy.sqrt
- numpy.square
- numpy.std
- numpy.subtract
- numpy.sum
- numpy.take
- numpy.tan
- numpy.tanh
- numpy.tile
- numpy.transpose
- numpy.tril
- numpy.triu
- numpy.true_divide
- numpy.trunc
- numpy.var
- numpy.vsplit
- numpy.where
- numpy.zeros_like
- numpy.zeros
- NumPy 상수
Tutorials
- Python Tutorial
- NumPy Tutorial
- Matplotlib Tutorial
- PyQt5 Tutorial
- BeautifulSoup Tutorial
- xlrd/xlwt Tutorial
- Pillow Tutorial
- Googletrans Tutorial
- PyWin32 Tutorial
- PyAutoGUI Tutorial
- Pyperclip Tutorial
- TensorFlow Tutorial
- Tips and Examples
numpy.random.standard_normal¶
numpy.random.standard_normal 함수는 표준정규분포(standard normal distribution)에서 샘플링한 난수를 반환합니다.
randn()과 기능이 비슷하지만 standard_normal()은 튜플을 인자로 받는다는 점에서 차이가 있습니다.
예제1¶
import numpy as np
a = np.random.standard_normal(5)
b = np.random.standard_normal((2, 3))
print(a)
print(b)
[-0.42157142 0.48708298 -0.72281046 -0.97076806 -0.84774571]
[[-1.11720756 0.6316911 0.02264546]
[ 1.49320609 0.66350065 0.2685298 ]]
a는 표준정규분포에서 샘플한 난수 5개의 어레이입니다.
b는 (2, 3) 형태의 난수 어레이입니다. 튜플의 형태로 (2, 3)의 형태를 입력해주었습니다.
예제2¶
표준정규분포 N(1, 0)이 아닌, 평균 \({\mu}\), 표준편차 \({\sigma}\) 를 갖는 정규분포 N(\({\mu}\), \({\sigma}\)2)의 난수를 샘플링하기 위해서는
\({\sigma}\) * np.random.standard_normal(…) + \({\mu}\) 와 같은 형태로 사용합니다.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
a = np.random.standard_normal(10000)
b = 5.0 * np.random.standard_normal(10000) - 2.5
plt.hist(a, bins=100, density=True, alpha=0.7, histtype='stepfilled')
plt.hist(b, bins=100, density=True, alpha=0.5, histtype='stepfilled')
plt.show()
a는 표준정규분포를 갖는 임의의 실수 10000개이고,
b는 표준편차 5.0, 평균 -2.5를 갖는 임의의 실수 10000개입니다.
matplotlib을 이용해서 분포를 확인해보면 아래와 같습니다.
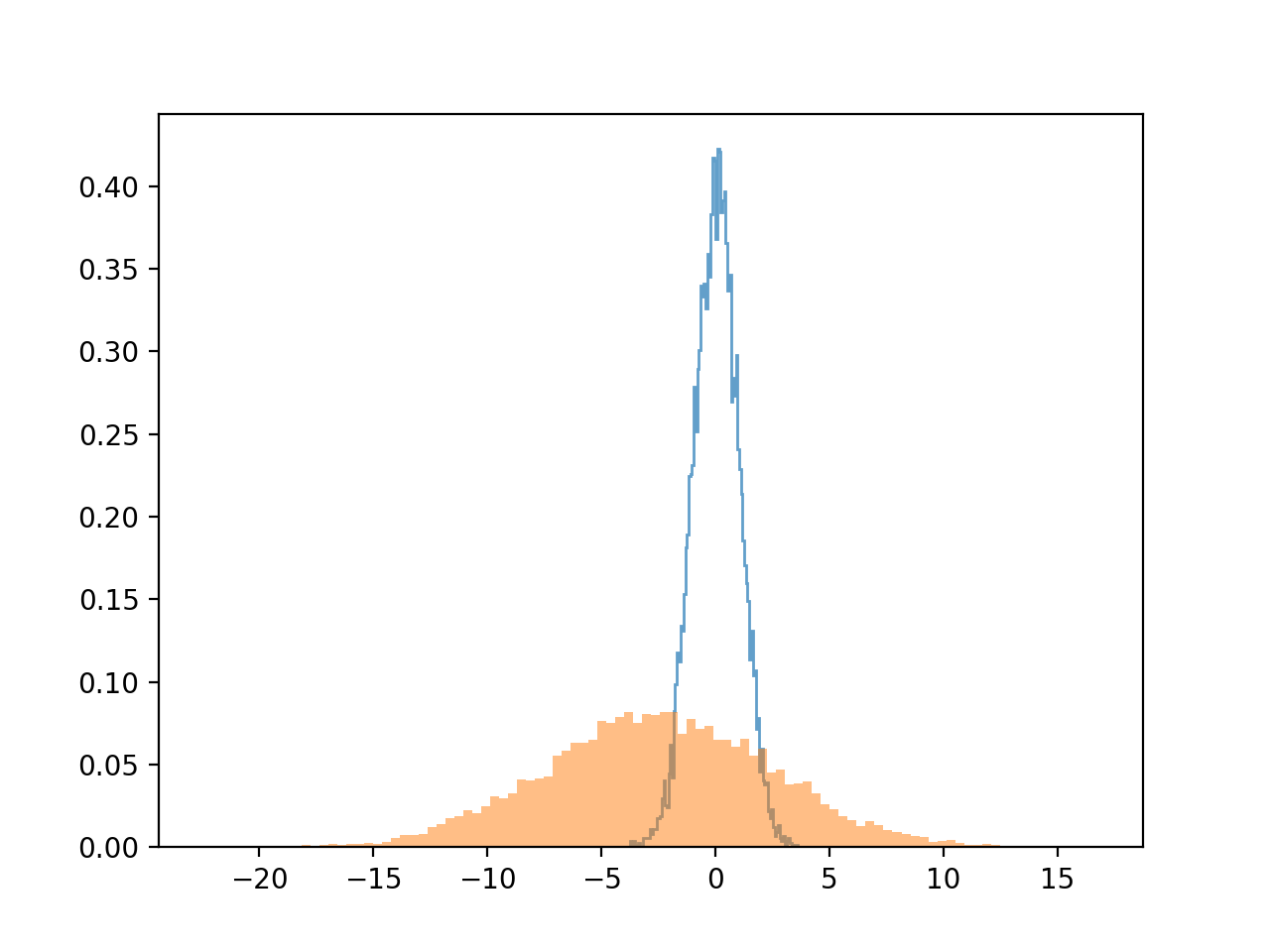
그림. numpy.random.standard_normal() 로 생성한 난수의 분포.¶
이전글/다음글
이전글 : numpy.random.seed
다음글 : numpy.reciprocal