Contents
- Matplotlib Tutorial - 파이썬으로 데이터 시각화하기
- Matplotlib 설치하기
- Matplotlib 기본 사용
- Matplotlib 숫자 입력하기
- Matplotlib 축 레이블 설정하기
- Matplotlib 범례 표시하기
- Matplotlib 축 범위 지정하기
- Matplotlib 선 종류 지정하기
- Matplotlib 마커 지정하기
- Matplotlib 색상 지정하기
- Matplotlib 그래프 영역 채우기
- Matplotlib 축 스케일 지정하기
- Matplotlib 여러 곡선 그리기
- Matplotlib 그리드 설정하기
- Matplotlib 눈금 표시하기
- Matplotlib 타이틀 설정하기
- Matplotlib 수평선/수직선 표시하기
- Matplotlib 막대 그래프 그리기
- Matplotlib 수평 막대 그래프 그리기
- Matplotlib 산점도 그리기
- Matplotlib 3차원 산점도 그리기
- Matplotlib 히스토그램 그리기
- Matplotlib 에러바 표시하기
- Matplotlib 파이 차트 그리기
- Matplotlib 히트맵 그리기
- Matplotlib 여러 개의 그래프 그리기
- Matplotlib 컬러맵 설정하기
- Matplotlib 텍스트 삽입하기
- Matplotlib 수학적 표현 사용하기
- Matplotlib 그래프 스타일 설정하기
- Matplotlib 이미지 저장하기
- Matplotlib 객체 지향 인터페이스 1
- Matplotlib 객체 지향 인터페이스 2
- Matplotlib 축 위치 조절하기
- Matplotlib 이중 Y축 표시하기
- Matplotlib 두 종류의 그래프 그리기
- Matplotlib 박스 플롯 그리기
- Matplotlib 바이올린 플롯 그리기
- Matplotlib 다양한 도형 삽입하기
- Matplotlib 다양한 패턴 채우기
- Matplotlib 애니메이션 사용하기 1
- Matplotlib 애니메이션 사용하기 2
- Matplotlib 3차원 Surface 표현하기
- Matplotlib 트리맵 그리기 (Squarify)
- Matplotlib Inset 그래프 삽입하기
Tutorials
- Python Tutorial
- NumPy Tutorial
- Matplotlib Tutorial
- PyQt5 Tutorial
- BeautifulSoup Tutorial
- xlrd/xlwt Tutorial
- Pillow Tutorial
- Googletrans Tutorial
- PyWin32 Tutorial
- PyAutoGUI Tutorial
- Pyperclip Tutorial
- TensorFlow Tutorial
- Tips and Examples
Matplotlib 텍스트 삽입하기¶
matplotlib.pyplot 모듈의 text() 함수는 그래프의 적절한 위치에 텍스트를 삽입하도록 합니다.
text() 함수를 사용해서 그래프 영역에 텍스트를 삽입하고, 다양하게 꾸미는 방법에 대해 소개합니다.
이 페이지에서 사용하는 히스토그램 예제는 히스토그램 그리기 페이지를 참고하세요.
Keyword: plt.text(), text, 텍스트 삽입
■ Table of Contents
1) 기본 사용¶
예제¶
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
a = 2.0 * np.random.randn(10000) + 1.0
b = np.random.standard_normal(10000)
c = 20.0 * np.random.rand(5000) - 10.0
plt.hist(a, bins=100, density=True, alpha=0.7, histtype='step')
plt.text(1.0, 0.35, '2.0*np.random.randn(10000)+1.0')
plt.hist(b, bins=50, density=True, alpha=0.5, histtype='stepfilled')
plt.text(2.0, 0.20, 'np.random.standard_normal(10000)')
plt.hist(c, bins=100, density=True, alpha=0.9, histtype='step')
plt.text(5.0, 0.08, 'np.random.rand(5000)-10.0')
plt.show()
text() 함수를 이용해서 3개의 히스토그램 그래프에 설명을 위한 텍스트를 각각 추가했습니다.
text()에 그래프 상의 x 위치, y 위치, 그리고 삽입할 텍스트를 순서대로 입력합니다.
결과는 아래와 같습니다.
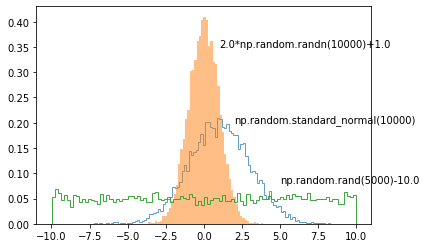
Matplotlib 텍스트 삽입하기 - 기본 사용¶
2) 텍스트 스타일 설정하기¶
예제¶
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
a = 2.0 * np.random.randn(10000) + 1.0
b = np.random.standard_normal(10000)
c = 20.0 * np.random.rand(5000) - 10.0
font1 = {'family': 'serif',
'color': 'darkred',
'weight': 'normal',
'size': 16}
font2 = {'family': 'Times New Roman',
'color': 'blue',
'weight': 'bold',
'size': 12,
'alpha': 0.7}
font3 = {'family': 'Arial',
'color': 'forestgreen',
'style': 'italic',
'size': 14}
plt.hist(a, bins=100, density=True, alpha=0.7, histtype='step')
plt.text(1.0, 0.35, 'np.random.randn()', fontdict=font1)
plt.hist(b, bins=50, density=True, alpha=0.5, histtype='stepfilled')
plt.text(2.0, 0.20, 'np.random.standard_normal()', fontdict=font2)
plt.hist(c, bins=100, density=True, alpha=0.9, histtype='step')
plt.text(5.0, 0.08, 'np.random.rand()', fontdict=font3)
plt.show()
fontdict 키워드를 이용하면 font의 종류, 크기, 색상, 투명도, weight 등의 텍스트 스타일을 설정할 수 있습니다.
font1, font2, font3과 같이 미리 지정한 폰트 딕셔너리를 fontdict 키워드에 입력해줍니다.
예제에서는 ‘family’, ‘color’, ‘weight’, ‘size’, ‘alpha’, ‘style’ 등과 같은 텍스트 속성을 사용했습니다.
Matplotlib에서 사용할 수 있는 텍스트 속성들에 대해서는 이 링크를 참고하세요.
결과는 아래와 같습니다.
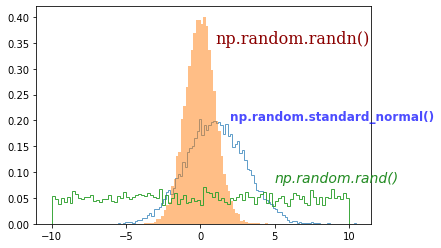
Matplotlib 텍스트 삽입하기 - 텍스트 스타일 설정하기¶
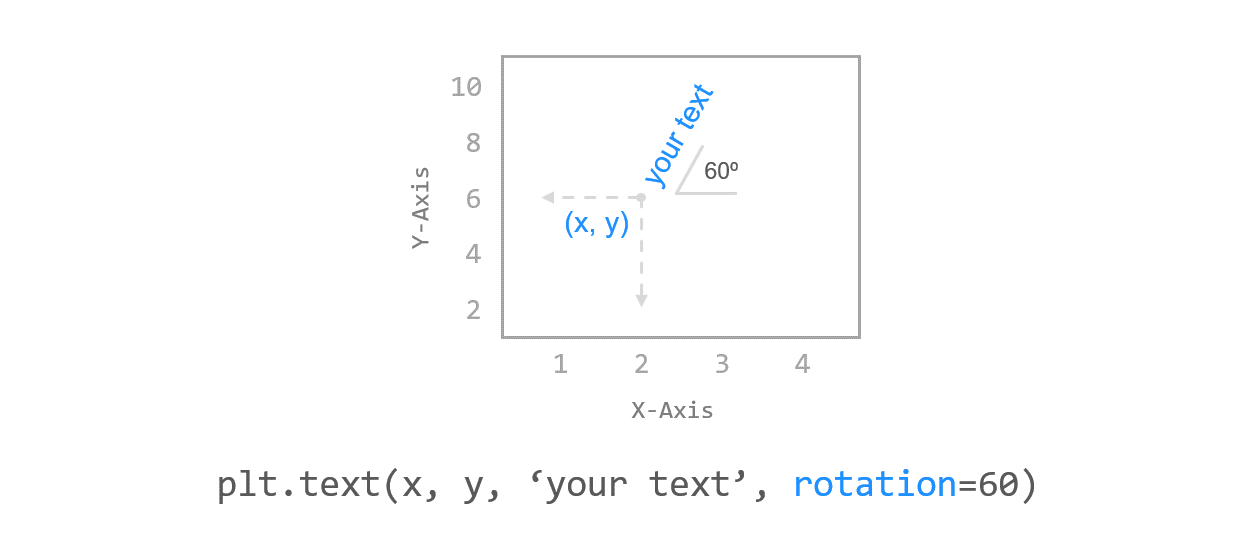
3) 텍스트 회전하기¶
예제¶
plt.hist(a, bins=100, density=True, alpha=0.7, histtype='step')
plt.text(-3.0, 0.15, 'np.random.randn()', fontdict=font1, rotation=85)
plt.hist(b, bins=50, density=True, alpha=0.5, histtype='stepfilled')
plt.text(2.0, 0.0, 'np.random.standard_normal()', fontdict=font2, rotation=-60)
plt.hist(c, bins=100, density=True, alpha=0.9, histtype='step')
plt.text(-10.0, 0.08, 'np.random.rand()', fontdict=font3)
plt.show()
rotation 키워드를 이용해서 텍스트를 회전할 수 있습니다.
첫번째, 두번째 텍스트를 각각 85도, -60도만큼 회전시켰습니다.
결과는 아래와 같습니다.
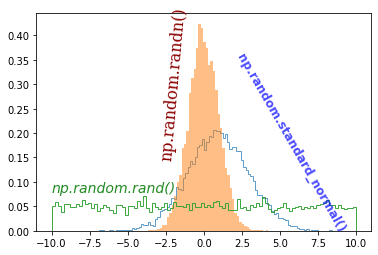
Matplotlib 텍스트 삽입하기 - 텍스트 회전하기¶
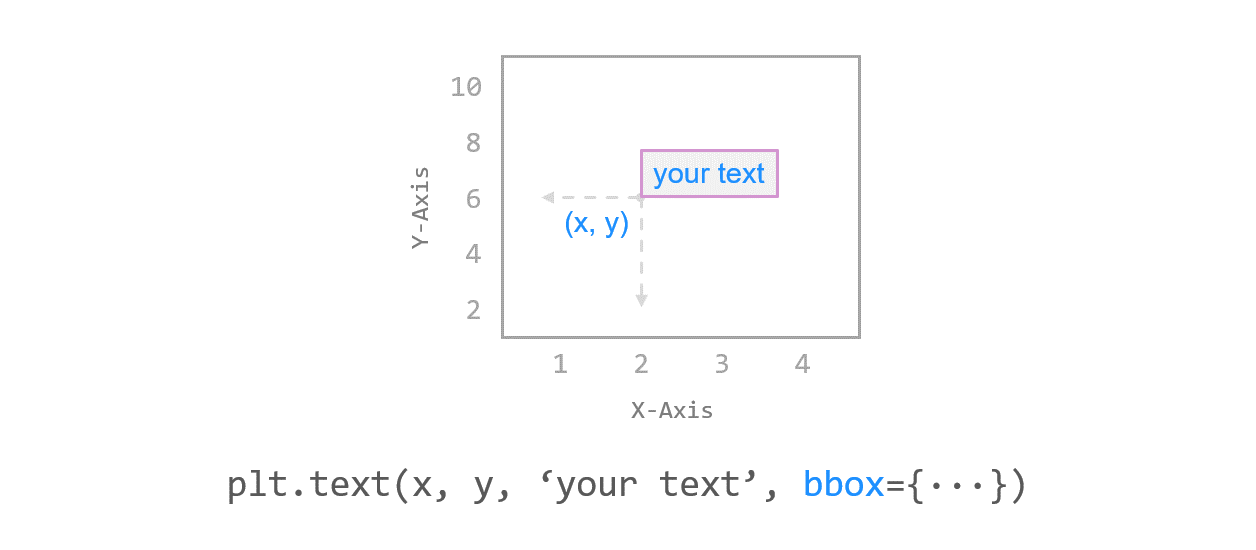
4) 텍스트 상자 스타일 설정하기¶
예제¶
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
a = 2.0 * np.random.randn(10000) + 1.0
b = np.random.standard_normal(10000)
c = 20.0 * np.random.rand(5000) - 10.0
font1 = {'family': 'serif',
'color': 'darkred',
'weight': 'normal',
'size': 16}
font2 = {'family': 'Times New Roman',
'color': 'blue',
'weight': 'bold',
'size': 12,
'alpha': 0.7}
font3 = {'family': 'Arial',
'color': 'forestgreen',
'style': 'italic',
'size': 14}
box1 = {'boxstyle': 'round',
'ec': (1.0, 0.5, 0.5),
'fc': (1.0, 0.8, 0.8)}
box2 = {'boxstyle': 'square',
'ec': (0.5, 0.5, 1.0),
'fc': (0.8, 0.8, 1.0),
'linestyle': '--'}
box3 = {'boxstyle': 'square',
'ec': (0.3, 1.0, 0.5),
'fc': (0.8, 1.0, 0.5),
'linestyle': '-.',
'linewidth': 2}
plt.hist(a, bins=100, density=True, alpha=0.7, histtype='step')
plt.text(-3.0, 0.15, 'np.random.randn()', fontdict=font1, rotation=85, bbox=box1)
plt.hist(b, bins=50, density=True, alpha=0.5, histtype='stepfilled')
plt.text(2.0, 0.0, 'np.random.standard_normal()', fontdict=font2, rotation=-60, bbox=box2)
plt.hist(c, bins=100, density=True, alpha=0.9, histtype='step')
plt.text(-10.0, 0.08, 'np.random.rand()', fontdict=font3, bbox=box3)
plt.show()
bbox 키워드를 사용해서 텍스트 상자의 스타일을 설정할 수 있습니다.
예제에서는 ‘boxstyle’, ‘ec’, ‘fc’, ‘linestyle’, ‘linewidth’ 등의 스타일을 사용했습니다.
‘ec’는 ‘edgecolor’, ‘fc’는 ‘facecolor’와 같습니다. 각각 텍스트 상자의 테두리와 면의 색을 지정하는 속성입니다.
결과는 아래와 같습니다.
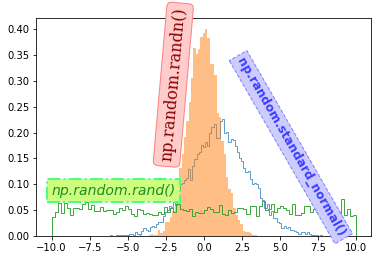
Matplotlib 텍스트 삽입하기 - 텍스트 상자 스타일 설정하기¶