Contents
- TensorFlow - 구글 머신러닝 플랫폼
- 1. 텐서 기초 살펴보기
- 2. 간단한 신경망 만들기
- 3. 손실 함수 살펴보기
- 4. 옵티마이저 사용하기
- 5. AND 로직 연산 학습하기
- 6. 뉴런층의 속성 확인하기
- 7. 뉴런층의 출력 확인하기
- 8. MNIST 손글씨 이미지 분류하기
- 9. Fashion MNIST 이미지 분류하기
- 10. 합성곱 신경망 사용하기
- 11. 말과 사람 이미지 분류하기
- 12. 고양이와 개 이미지 분류하기
- 13. 이미지 어그멘테이션의 효과
- 14. 전이 학습 활용하기
- 15. 다중 클래스 분류 문제
- 16. 시냅스 가중치 얻기
- 17. 시냅스 가중치 적용하기
- 18. 모델 시각화하기
- 19. 훈련 과정 시각화하기
- 20. 모델 저장하고 복원하기
- 21. 시계열 데이터 예측하기
- 22. 자연어 처리하기 1
- 23. 자연어 처리하기 2
- 24. 자연어 처리하기 3
- 25. Reference
- tf.cast
- tf.constant_initializer
- tf.constant
- tf.keras.activations.exponential
- tf.keras.activations.linear
- tf.keras.activations.relu
- tf.keras.activations.sigmoid
- tf.keras.activations.softmax
- tf.keras.activations.tanh
- tf.keras.datasets
- tf.keras.layers.Conv2D
- tf.keras.layers.Dense
- tf.keras.layers.Dropout
- tf.keras.layers.Flatten
- tf.keras.layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D
- tf.keras.layers.InputLayer
- tf.keras.layers.Maximum
- tf.keras.layers.Minimum
- tf.keras.layers.ZeroPadding2D
- tf.keras.metrics.Accuracy
- tf.keras.metrics.BinaryAccuracy
- tf.keras.Sequential
- tf.linspace
- tf.ones_initializer
- tf.ones
- tf.random_normal_initializer
- tf.random.normal
- tf.random.set_seed
- tf.random_uniform_initializer
- tf.random.uniform
- tf.range
- tf.rank
- tf.TensorShape
- tf.zeros_initializer
- tf.zeros
Tutorials
- Python Tutorial
- NumPy Tutorial
- Matplotlib Tutorial
- PyQt5 Tutorial
- BeautifulSoup Tutorial
- xlrd/xlwt Tutorial
- Pillow Tutorial
- Googletrans Tutorial
- PyWin32 Tutorial
- PyAutoGUI Tutorial
- Pyperclip Tutorial
- TensorFlow Tutorial
- Tips and Examples
tf.keras.activations.relu¶
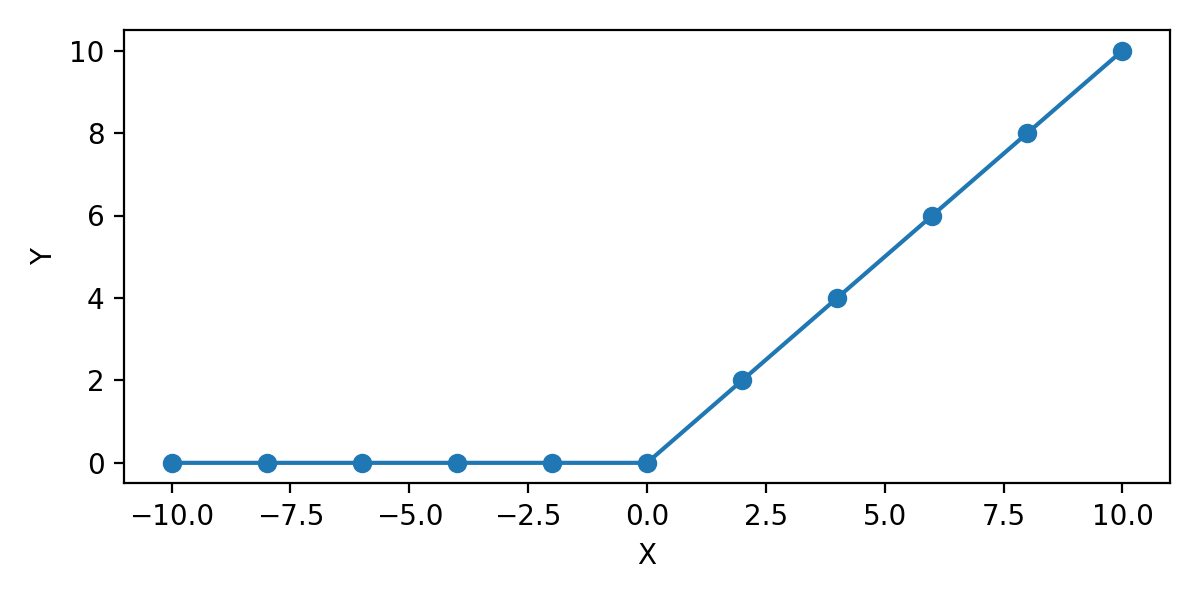
tf.keras.activations.relu는 ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit) Activation 함수를 적용합니다.
예제1¶
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (6, 3)
x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 11)
y = tf.keras.activations.relu(x).numpy()
print(x)
print(y)
plt.plot(x, y, 'o-')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
[-10. -8. -6. -4. -2. 0. 2. 4. 6. 8. 10.]
[ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 2. 4. 6. 8. 10.]
tf.keras.activations.relu는 ReLU 함수를 적용합니다.
기본적으로 입력값이 양수일 경우 y=x, 음수일 경우 y=0이 됩니다.
0을 기준으로 활성화 여부가 결정되며 이 값을 ‘threshold’라고 합니다.
예제2¶
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (6, 3)
x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 21)
y0 = tf.keras.activations.relu(x).numpy()
y1 = tf.keras.activations.relu(x, alpha=0.5).numpy()
y2 = tf.keras.activations.relu(x, max_value=5).numpy()
y3 = tf.keras.activations.relu(x, threshold=5).numpy()
plt.plot(x, y1, 'o-', label='alpha=0.5')
plt.plot(x, y2, 'o-', label='max_value=5')
plt.plot(x, y3, 'o-', label='threshold=5')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
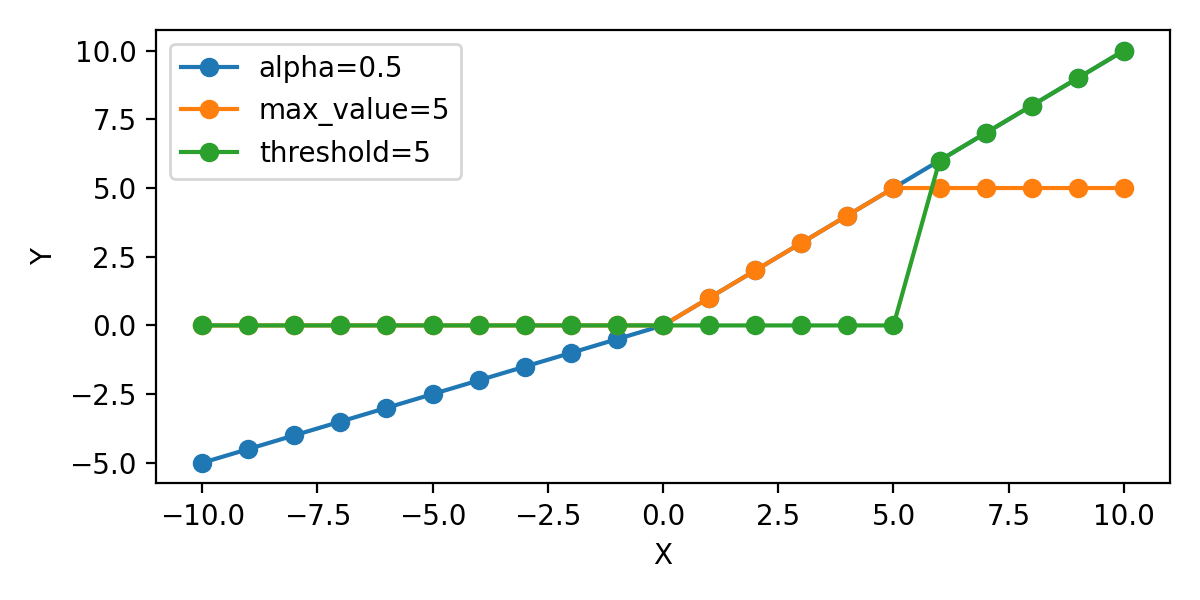
tf.keras_activations_relu 함수의 alpha, max_value, threshold 값을 지정할 수 있습니다.
alpha는 threshold 아래의 기울기를 지정합니다.
max_value는 출력값의 최대값을 제한합니다.
threshold는 threshold를 지정합니다.