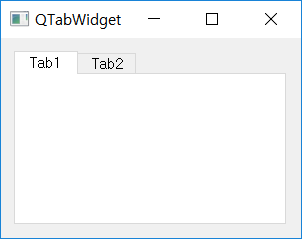
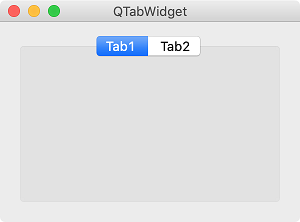
QTabWidget¶
While using GUI program, you may find a window with a tab as shown in the picture above. These tabs can be useful because the components in the program do not occupy a large area and can be classified into categories.
We’ll create a widget with two tabs in this example.
Example¶
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import (QApplication, QWidget, QTabWidget, QVBoxLayout)
class MyApp(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
tab1 = QWidget()
tab2 = QWidget()
tabs = QTabWidget()
tabs.addTab(tab1, 'Tab1')
tabs.addTab(tab2, 'Tab2')
vbox = QVBoxLayout()
vbox.addWidget(tabs)
self.setLayout(vbox)
self.setWindowTitle('QTabWidget')
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 300, 200)
self.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = MyApp()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
A small widget with two tabs is created.
Description¶
tab1 = QWidget()
tab2 = QWidget()
We created two widgets to be located on each tab.
tabs = QTabWidget()
tabs.addTab(tab1, 'Tab1')
tabs.addTab(tab2, 'Tab2')
Use QTabWidget() to create tabs and use addTab() to add Tab1 and Tab2 to the tabs.
vbox = QVBoxLayout()
vbox.addWidget(tabs)
self.setLayout(vbox)
Create a vertical box layout and insert a tab widget. Then set the vertical box as the layout of the widget.
Prev/Next
Prev : QGroupBox
Next : QTabWidget (Advanced)